In this blog we will see system information commands along with disk usage command.
System Information Commands
- date :- This command is used to display the system date and time. date command is also used to set date and time of the system.
$ date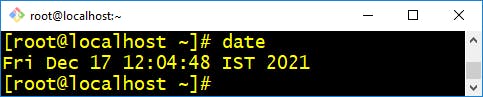
- cal :- This command is a calendar command in Linux which is used to see the calendar of a specific month or a whole year.
$ cal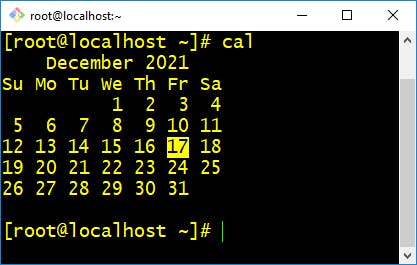
- uptime :- It is used to find out how long the system is active (running)
$ uptime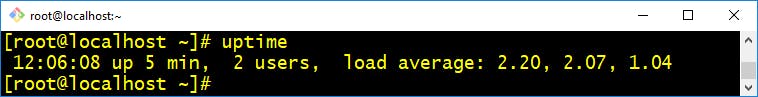
- w :- This command in Linux is used to show who is logged on and what they are doing. This command shows the information about the users currently on the machine and their processes.
$ w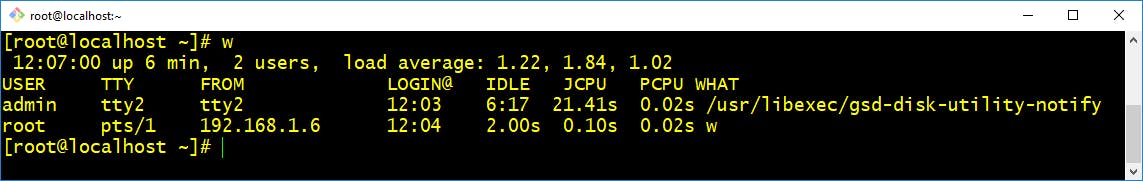
- whoami :- It is a concatenation of the words "Who am I?" and prints the effective username of the current user when invoked.
$ whoami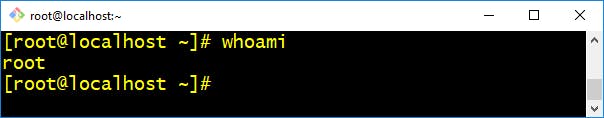
- finger :- Finger command is a user information lookup command which gives details of all the users logged in. This tool is generally used by system administrators. It provides details like login name, user name, idle time, login time, and in some cases their email address even.
$ fingure - uname :- It prints all the system information in the following order: Kernel name, network node hostname, kernel release date, kernel version, machine hardware name, hardware platform, operating system.
$ uname -a
- timedatectl :- The timedatectl command allows you to query and change the configuration of the system clock and its settings, you can use this command to set or change the current date, time, and timezone or enable automatic system clock synchronization with a remote NTP server.
$ timedatectl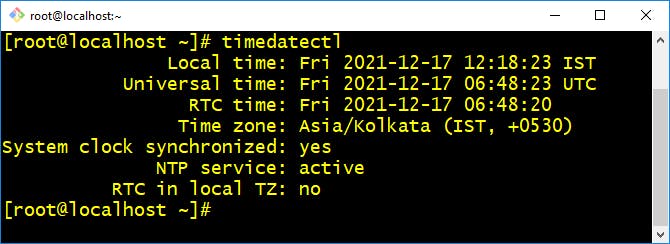
- last reboot :- Shows system history of last reboot.
$ last reboot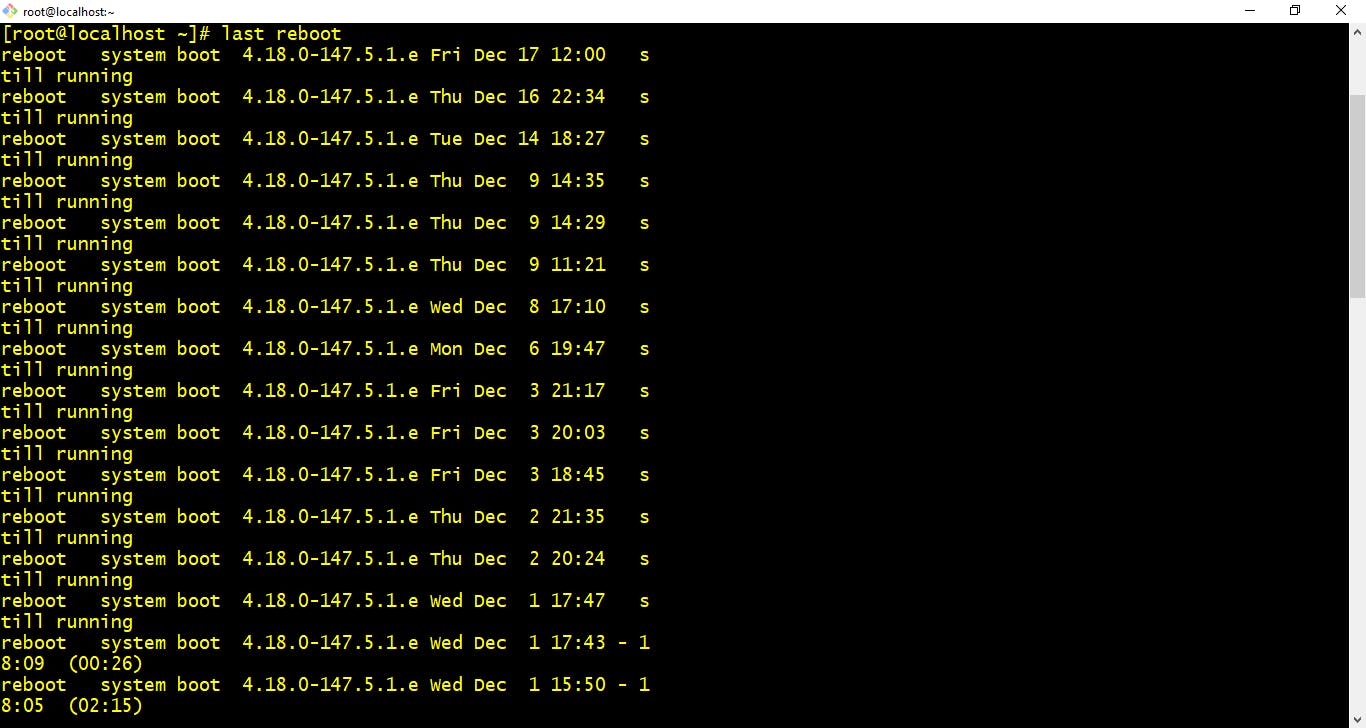
- whereis :- This command is used to find the location of source/binary file of a command and manuals sections for a specified file in Linux system.
$ whereis <application name>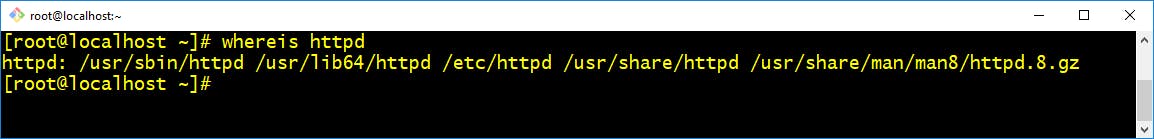
- which :- This command in Linux is a command which is used to locate the executable file associated with the given command by searching it in the path environment variable.
$ which <application name>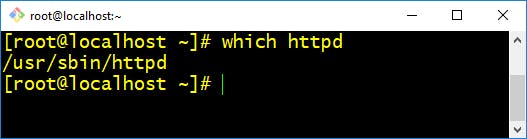
- hostname :- This command in Linux is used to obtain the DNS(Domain Name System) name and set the system’s hostname or NIS(Network Information System) domain name.
$ hostname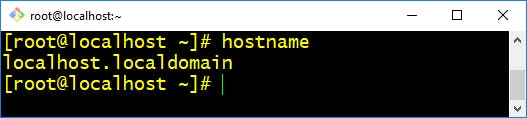 It is very important and recommended to use "man" command for every linux command we use as this command in Linux is used to display the user manual of any command that we can run on the terminal. It provides a detailed view of the command which includes NAME, SYNOPSIS, DESCRIPTION, OPTIONS, EXIT STATUS, RETURN VALUES, ERRORS, FILES, VERSIONS, EXAMPLES, AUTHORS. Make sure to go through below commands for better understanding.
It is very important and recommended to use "man" command for every linux command we use as this command in Linux is used to display the user manual of any command that we can run on the terminal. It provides a detailed view of the command which includes NAME, SYNOPSIS, DESCRIPTION, OPTIONS, EXIT STATUS, RETURN VALUES, ERRORS, FILES, VERSIONS, EXAMPLES, AUTHORS. Make sure to go through below commands for better understanding. $ man date$ man cal$ man uptime$ man w$ man whoami$ man fingure$ man uname$ man timedatectl$ man last reboot$ man whereis$ man which$ man hostname
Hardware And Disk Usage Commands
- cat /proc/cpuinfo :- This command provides you CPU information of the system.
$ cat /proc/cpuinfo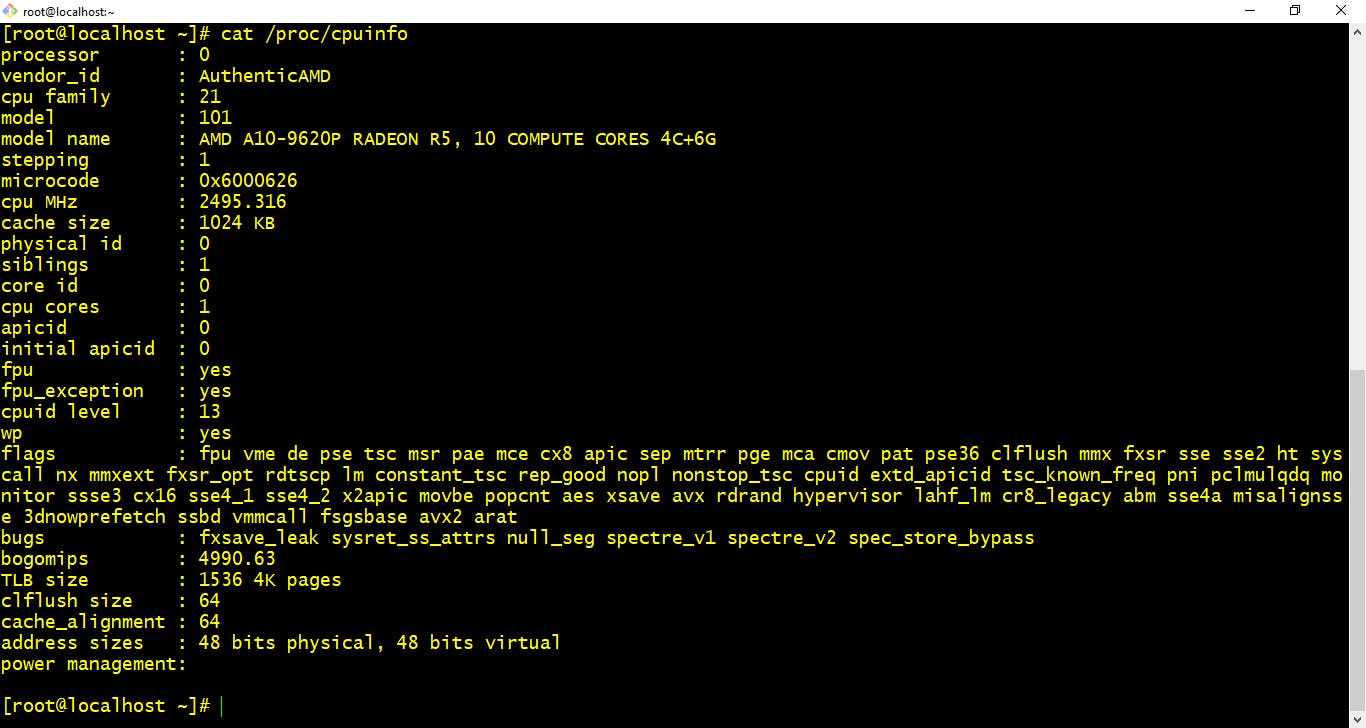
- cat /proc/meminfo :-This command provides you memory information of the system.
$ cat /proc/meminfo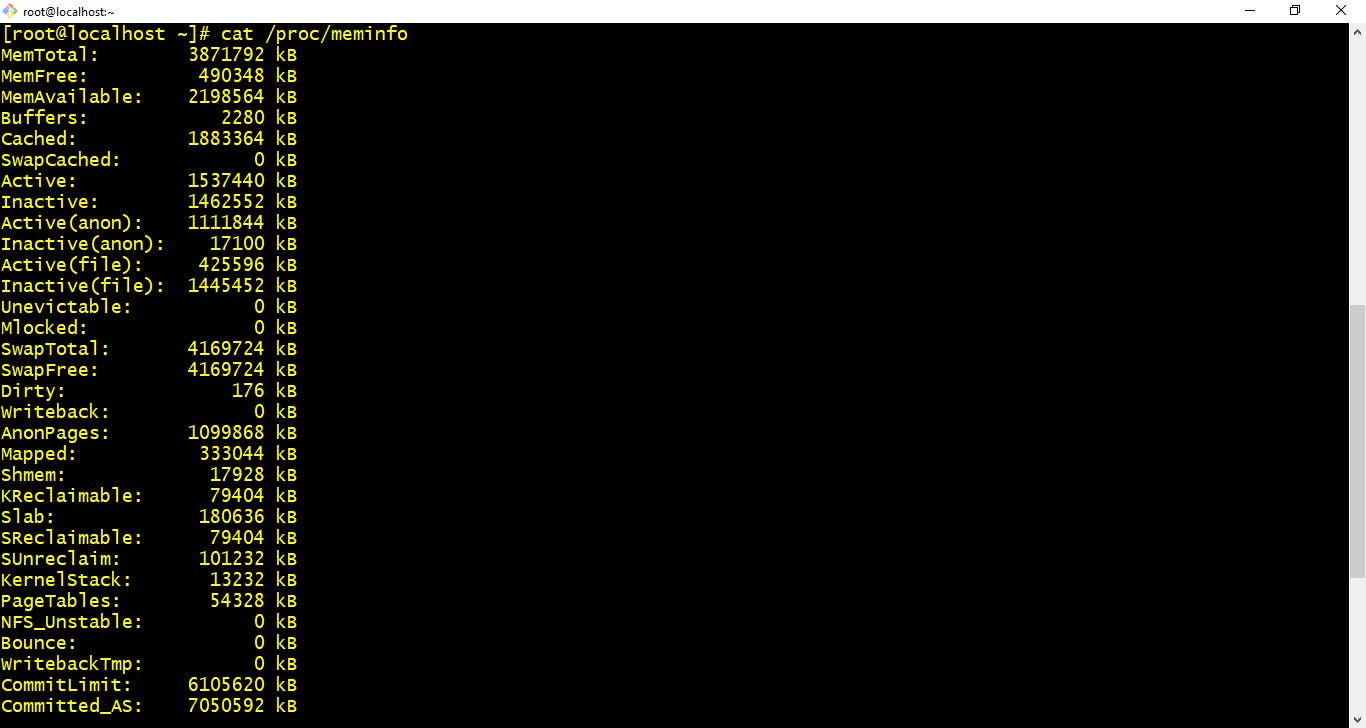
- lsblk :- Displays block devices related infromation.
$ lsblk
- blkid :- This command allows you to display information about available block devices.
$ blkid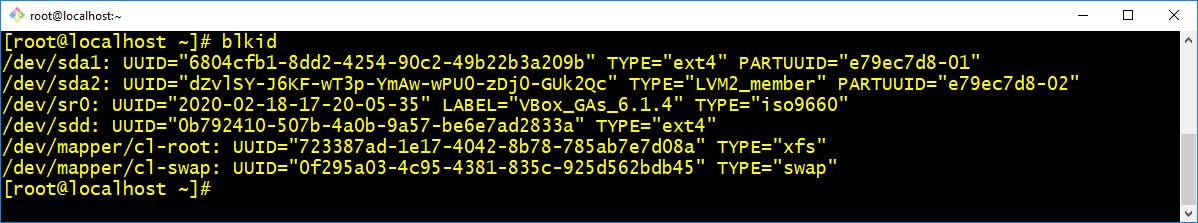
- fdisk -l :- Shows disk partitions sizes and type.
$ fdisk -l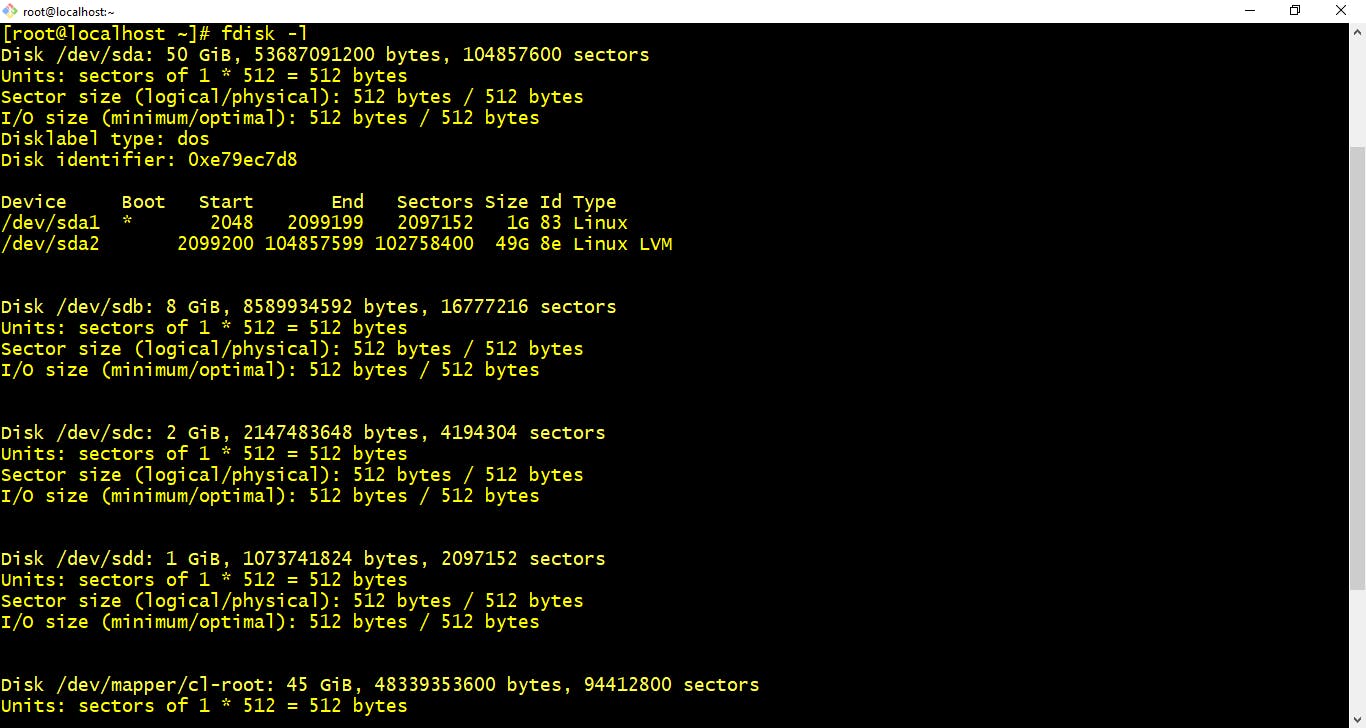
- df :- Linux df command is used to display the disk space used in the file system. The 'df' stands for "disk filesystem." It defines the number of blocks used, the number of blocks available, and the directory where the file system is mounted.
Example:- Display free space on mounted system$ df -h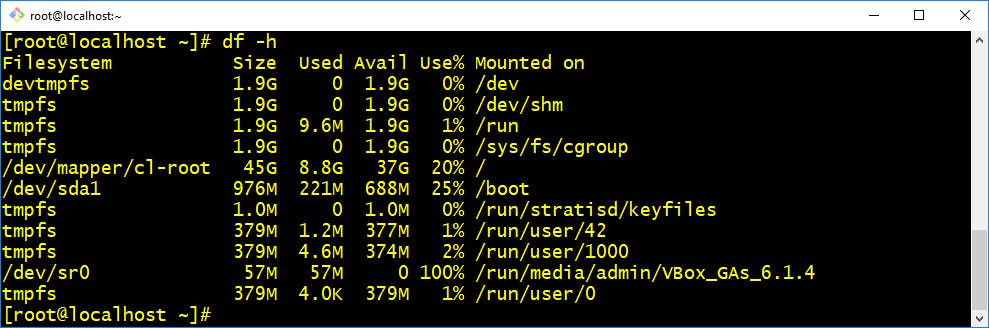 Example:- Display free inodes on file systems
Example:- Display free inodes on file systems$ df -i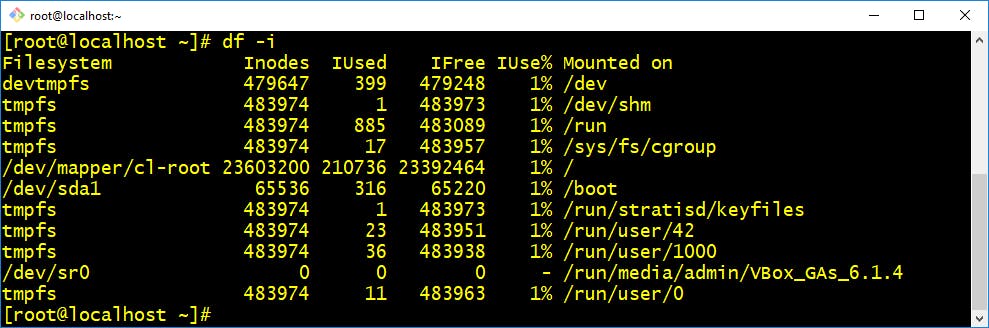
- du :- command, short for disk usage, is used to estimate file space usage.
The du command can be used to track the files and directories which are consuming excessive amount of space on hard disk drive.
$ du -sh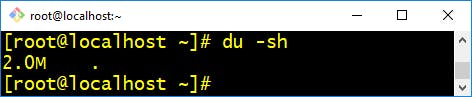
- findmnt :- This command will list all mounted filesystems or search for a filesystem. The findmnt command is able to search in /etc/fstab, /etc/mtab or /proc/self/mountinfo. If device or mountpoint is not given, all filesystems are shown.
$ findmnt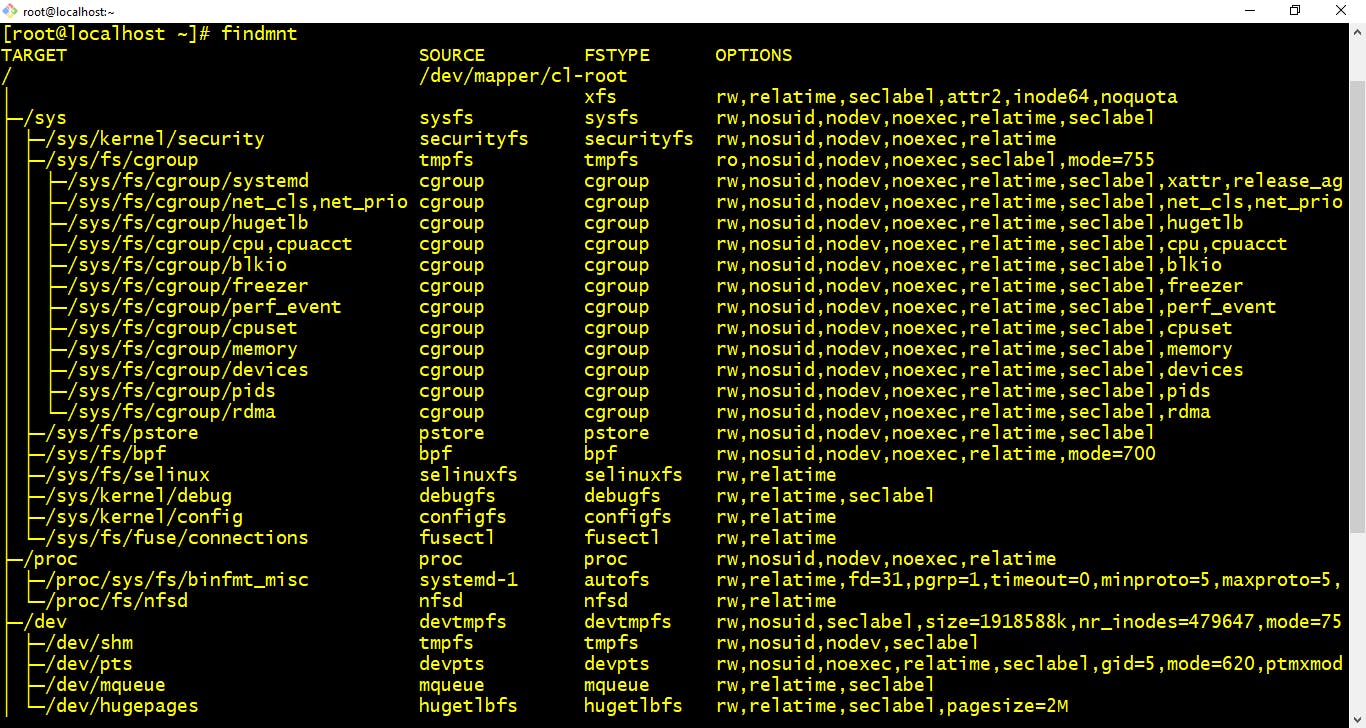 Make sure to check man pages for this these commands as listed below for better understanding.
Make sure to check man pages for this these commands as listed below for better understanding.$ man lsblk$ man blkid$ man fdisk$ man df$ man du$ man findmnt
